Calibration adjusts current content and figures to the standard content and figures.
Calibration refers to the alignment of touched points with cursor location (coordinate value).
There are many types of touch screens. Although some do not require calibration, many touch screens require calibration before use.
Calibration is usually performed on the setting screen of a device driver (mouse emulation software). There are two methods of calibrating DMC touch controllers. One is to calibrate by host PC and save calibration data in the host PC. The other is to calibrate by controller and save the calibration data in the EEPROM on the controller. In both cases, calibration is performed on the monitor screen. The difference in features and operations are described below.
There are many types of touch screens. Although some do not require calibration, many touch screens require calibration before use.
[Features] Multiple calibration functions are executed by a powerful CPU.
Example 1: Manufacturing machine with 2 monitors. Calibration functions are executed in the driver.

Example 2: Embedded machine. Calibration is executed inside the controller (EEPROM Calib. mode).
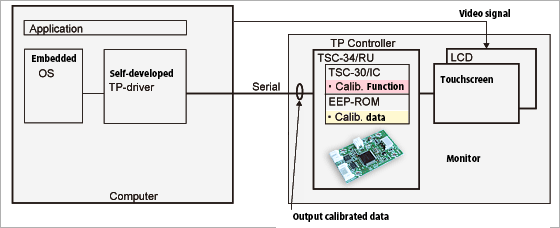
- [Features]
- ・Driver development load such as for embedded devices is smaller.
- ・Calibration data is saved in the TP controller inside the monitor of a touch screen. Therefore, when the monitor is replaced, re-calibration is unnecessary.